About Us
The Multiscale Muscle Mechanophysiology (M3) lab is collectively fascinated by skeletal muscles, which are the motors for all the wide range of voluntary movements in the human body. Each muscle’s properties are beautifully tuned for a specific function in the body, which can be easily disrupted by diseases such as muscular dystrophy, cerebral palsy, or in aging populations. We seek to gain new insights into the form, function, biology, and diseases of muscles. Our work has the ultimate goal of improving treatments and quality of life for individuals suffering from muscle-related clinical problems. We integrate a variety of computational and experimental approaches to achieve this goal.Selected Publications
-
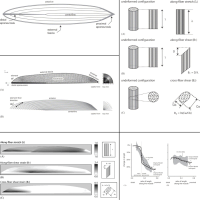
A 3D model of muscle reveals the causes of nonuniform strains in the biceps brachii
Biomechanical models generally assume that muscle fascicles shorten uniformly. However, dynamic magnetic resonance images of the biceps brachii have shown nonuniform shortening along some muscle fascicles during low-load elbow flexion. The purpose of this study was to uncover the features of the biceps brachii architecture and material properties that could lead to nonuniform shortening. We created a three-dimensional finite-element model of the biceps brachii and compared the tissue strains predicted by the model with experimentally measured tissue strains.
-
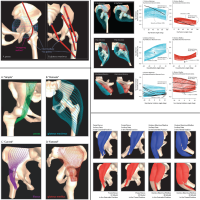
Three-Dimensional Representation of Complex Muscle Architectures and Geometries
Almost all computer models of the musculoskeletal system simplify muscle geometry. This simplification (i) limits the ability of models to accurately represent the paths of muscles with complex geometry and (ii) assumes that moment arms are equivalent for all fibers within a muscle or muscle compartment. The goal of this work was to develop and evaluate a new method for creating three-dimensional finite-element models that represent complex muscle geometry and the variation in moment arms across fibers within a muscle. We created 3D models of the psoas, iliacus, gluteus maximus, and gluteus medius muscles from magnetic resonance images.


